It was around 2009 when I was finally ready to abandon the time-honored diet-heart hypothesis. I remember wondering if I’d be excommunicated from the medical community, i.e., lose my medical license due to heresy. In a nutshell, the diet-heart hypothesis to which I refer was the idea that dietary saturated fat was the clear-cut cause of coronary artery disease and associated heart attacks, angina pectoris (reversible heart pains), and cardiac deaths. (Also strokes and peripheral arterial disease.)
My re-evaluation of the evidence lead me to create the world’s first ketogenic Mediterranean diet, which is included in the 2nd edition of my Advanced Mediterranean diet and Conquer Diabetes and Prediabetes. Search Amazon.com and you’ll find several other subsequent ketogenic Mediterranean diet books; I wonder if any of them cited my work.
Dr. Axel Sigurdsson recently wrote an updated history of the diet-heart hypothesis, focusing on the downfall of the hypothesis and the role of George Mann, whom I’d swear I never heard of. An excerpt:
Ancel Keys changed the world. He was right about many things—that lifestyle matters, that food affects disease, that public health can’t afford to wait forever. But in boiling heart disease down to a single nutrient, he oversimplified a complex truth. His hypothesis became policy before it was fully proven. And once policy hardens, it resists correction.
George Mann was no savior. His critiques were often bombastic, his tone combative. But beneath the fire was a warning science should have heeded: that premature consensus can blind, that evidence must lead—not politics, not personalities, not the noise of institutional momentum.
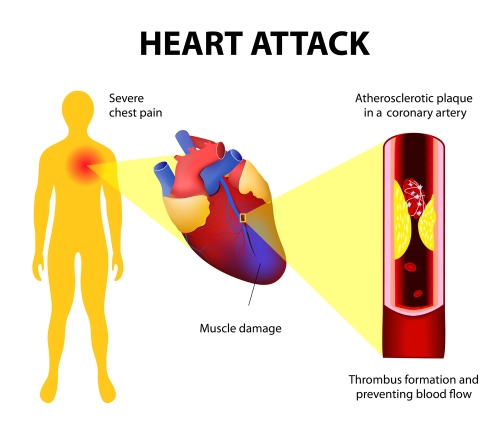
I recommend the entire article to you. I suspect AI (artificial intelligence) was utilized, mainly judging from the three pictures. Dr. Sigurdsson has been publishing some great articles recently, and I believe credited AI in some of them, which is OK by me.
Steve Parker, M.D.